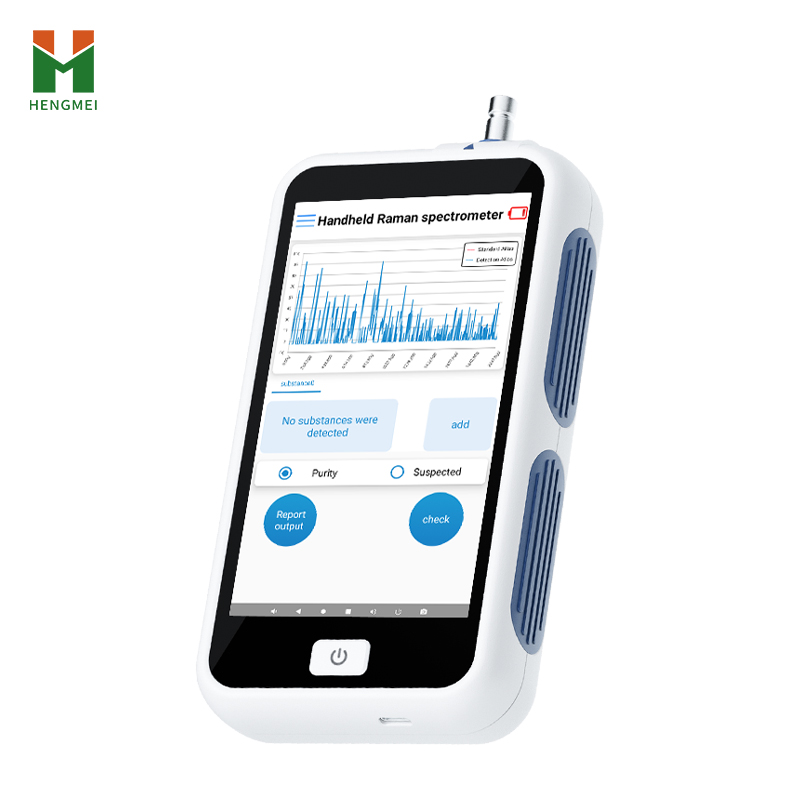
In today's rapidly evolving field of analytical testing, handheld Raman spectrometer has become a vital tool for rapid on-site material identification. This portable analytical device, based on the principle of Raman scattering, provides accurate and reliable material composition information within seconds, overcoming the limitations and delays associated with traditional laboratory analysis.
The core value of handheld Raman spectrometers lies in their portability, speed, and non-destructive testing capabilities. Compared to traditional large laboratory equipment, they can be brought directly to the sample site, require no complex sample preparation, and deliver results through simple "point-and-shoot" operation. This ability to obtain instant data makes them indispensable in fields such as food safety, pharmaceutical raw material identification, gemstone testing, and industrial material analysis.
Principles of Raman Spectroscopy and Instrument Composition
1.Physical Basis of Raman Scattering
Raman spectroscopy is based on the phenomenon of Raman scattering discovered by Indian scientist C.V. Raman in 1928. When monochromatic laser light irradiates a sample, most photons undergo elastic scattering (Rayleigh scattering), retaining their original energy; approximately one in a million photons undergo inelastic scattering (Raman scattering), with altered energy. This energy change corresponds to the vibrational and rotational energy level transitions of the sample molecules, forming a unique "molecular fingerprint" spectrum.
Handheld Raman spectrometers utilize this principle by measuring these weak Raman scattered photons to obtain molecular structural information of the sample.
2.Core Components and Technical Features
Handheld Raman spectrometers typically consist of the following key components:
Laser source: 785 nm semiconductor laser, power adjustable from 0-500 mW, linewidth <0.08 nm
Optical system: Miniature confocal design, spectral resolution up to 5 cm⁻¹
Detector: High-sensitivity detector
Technical Advantages and Innovative Breakthroughs
1.Portability and Environmental Adaptability
Weight ≤0.8 kg: Can be operated with one hand, suitable for outdoor, workshop, and other complex environments.
IP67 protection rating: Dustproof and waterproof, adaptable to high-humidity and dusty scenarios.
2.Efficient Detection and Intelligent Interaction
3-second rapid detection: Spectral acquisition can be completed with 500 ms integration time.
5.5-inch touchscreen: Android system supports one-click operation and data visualization.
GPS positioning + 13-megapixel camera: Records detection location and sample images for easy traceability.
3.Cloud and Data Management
Wireless transmission (WiFi/4G): Test data can be uploaded in real-time to regulatory platforms.
Private deployment: Enterprises can customize databases to meet confidentiality needs.
16G storage + PDF reports: Supports massive local data storage and batch export.
4.High Precision and Reliability
Spectral range 200-3800 cm⁻¹: Covers characteristic peaks of most organic and inorganic substances.
Adjustable laser power (0-500 mW): Adapts to samples with different fluorescence intensities.
Repeatability error <1%: Meets laboratory-level testing requirements.
Common Faults and Solutions
1.Strong fluorescence and weak signal when measuring glass-packaged samples using the probe cap?
Answer: This may be due to thick glass walls and strong fluorescence signals from the glass. Try using a quartz container for measurement.
2.Sample cannot be matched to the spectral library?
Answer: ① The laser intensity setting may be too low; generally, set it to 80 for detection.
② The detection threshold may be set too high; it should ideally be set at 0.92.
③ Check if the search range is selected.
④ If the sample is not in the spectral library, add the newly tested sample to the library.
3.Unable to power on?
Answer: The battery may be depleted; recharge it.
4.Occasional abnormal spectra?
Answer: This may be due to electromagnetic noise interference; move away from areas with severe electromagnetic interference.
5.Slow detection speed?
Answer: ① The integration time may be too long.
② Check if cloud detection is enabled (takes about 15 seconds).
6.Misidentification?
Answer: The test sample may have extremely high similarity to a spectrum in the library. Add the newly tested sample to the library to resolve this.
Handheld Raman spectrometers, with their technical advantages and application value, have become essential tools in modern analytical testing. From food safety to material analysis, they are transforming traditional testing models, enabling a paradigm shift from "laboratory analysis" to "on-site instant detection."
Article address:https://www.spectrometer.top/news/41.html


 Current
location:
Current
location: